

Transfection Reagent
Convoy™ Transfection Reagent
G-418 (aminoglycosidic Antibiotic)
ConvoyTMTransfection Reagent Detail Transfection Protocol Product Literature
ConvoyTM is new generation cationic polymer gene transfection reagent. It has several unique features necessary for efficient transfection – DNA condensation and endosomal release, which improves gene transfection efficiency.
Compared with cationic lipids, cationic polymers are extremely stable, easy to handle, and more resistant to serum in cell culture.
The above advantages make gene transfection much easier and reproducible. ConvoyTM is widely used for both primary cell and established cell lines.
Feature Highlights:– High transfection efficiency
Under comparison with other commercial brands in the U.S., ConvoyTM is more stable both in presence and absence of serum, and shows higher transfection efficiency than cationic lipid in some most commonly used cell lines.
Convoy TM shows especially higher transfection efficiency in HUVEC (primary cell), which is insensate to most transfection reagents including cationic lipids.
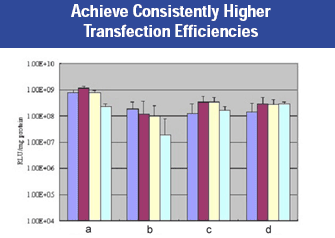
Figure 1: The pCMV-luc plasmid was transfected into HEK 293 cells and then assayed for luciferase activity 48 hours post-transfection. Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent; Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent: Panel (c): competitor B transfection reagent: Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
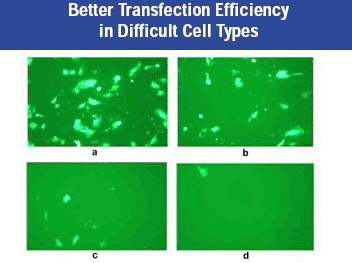 Figure 2: HUVEC cells transfection (100x magnification).Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent; Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent; Panel (c): Competitor B trasnfection reagent; Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent
Figure 2: HUVEC cells transfection (100x magnification).Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent; Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent; Panel (c): Competitor B trasnfection reagent; Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent
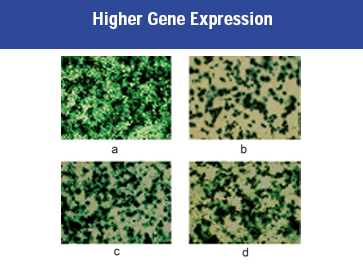 Figure 3: HEK 293 cells were transfected with plasmid DNA containing lacZ gene. Cells incorporating lacZ gene metabolize X-Gal and are stained blue. Cells were assayed 48 hrs post transfection. Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent; Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent; Panel (c): Competitor B transfection reagent; Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
Figure 3: HEK 293 cells were transfected with plasmid DNA containing lacZ gene. Cells incorporating lacZ gene metabolize X-Gal and are stained blue. Cells were assayed 48 hrs post transfection. Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent; Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent; Panel (c): Competitor B transfection reagent; Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
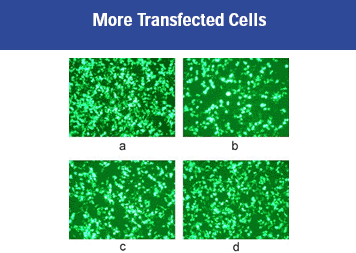 Figure 4: HEK 293 cells transfected with pEGFPN1 and shown 48 hrs post transfection (100x magnification). Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent; Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent; Panel (c): Competitor B transfection reagent; Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
Figure 4: HEK 293 cells transfected with pEGFPN1 and shown 48 hrs post transfection (100x magnification). Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent; Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent; Panel (c): Competitor B transfection reagent; Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
– Low Cytotoxicity
The cell survival rate is over 90%, when the experiment is carried in suitable condition and with recommended ConvoyTM dosage.
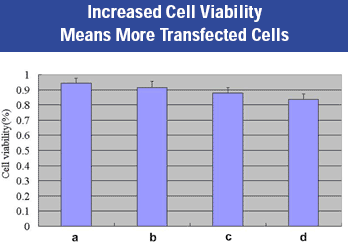 Figure 5: The viability of HEK 293 cells was assessed using MTT method 48 hrs post transfection. Each transfection reagent was used under optimal conditions. Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent: Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent: Panel (c): Competitor B transfection reagent: Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
Figure 5: The viability of HEK 293 cells was assessed using MTT method 48 hrs post transfection. Each transfection reagent was used under optimal conditions. Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent: Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent: Panel (c): Competitor B transfection reagent: Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
– Simplified Protocol < 30 minutes Detail Transfection Protocol
As a serum resistant reagent, the transfection procedure is very simple: the DNA/transfection reagent complexes can be directly added into complete cell medium and waited for transfection assay (See Protocol Link above). With no need to change medium, the transfection can be finished in half an hour, and the whole procedure is simple, short and flexible. Additionally, cytotoxicity is found to be lower with ConvoyTM by carrying out the simplified shortened protocol.
– Compatibility with most cell lines
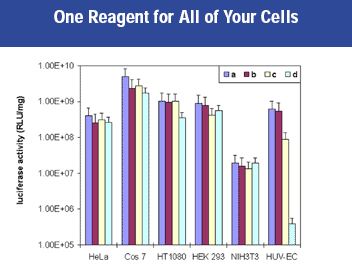 Figure 6: The pCMB-luc plasmid was transfected into a number of cell lines. The cells were then assayed for luciferase activity 48 hrs post transfection. Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent: Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent: Panel (C): Competitor B transfection reagent: Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
Figure 6: The pCMB-luc plasmid was transfected into a number of cell lines. The cells were then assayed for luciferase activity 48 hrs post transfection. Panel (a): Convoy™ Transfection Reagent: Panel (b): Competitor A transfection reagent: Panel (C): Competitor B transfection reagent: Panel (d): Competitor C transfection reagent.
Cell lines (not limited to below) successfully transfected using Convoy™
| Cell line | Origin | Cell type |
| HEK 293 | Human | Embryonic kidney |
| HeLa | Human | Cervix carcinoma |
| NIH 3T3 | Mouse | Embryo fibroblast |
| BNL CL2 | Mouse | Embryonic kidney cells |
| HepG2 | Human | Hepatocarcinoma |
| COS7 | Monkey | SV40 kidney transformed |
| CHO | Chinese hamster | Ovary |
| 5HSY-5Y | Human | Neuroblastoma |
| IMR 32 | Human | Neuroblastoma |
| MRC5 | Human | Fetal lung epithelium |
| MCF7 | Human | Breast adenocarcinoma |
| K562 | Human | Chronic leukemia |
| SKOV-3 | Human | Ovarian adenocarcinoma |
| IGROV-1 | Human | Ovarian adenocarcinoma |
| HUVEC (primary cell) | Human | Umbilical endothelial cell |
Looking for more data? Please visit Detail Transfection Protocol or simply contact us.
G-418 (aminoglycosidic Antibiotic) – suggested item for transfection experiments
G-418 sulfate
Aminoglycosidic antibiotic
White powder, shipped at room temperature, dry powder stored at RT and solution at -20°C.
Formula: C20H40N4O10¡¤2H2SO4 (CAS No.: 108321-42-2)
Molecular weight: 692.71
Purpose: Acts by interfering with protein synthesis and is usually used as an agent for selection of cultured cells expressing a gene that confers resistance to G-418.
For research use only. Not for human or drug use.